Your Guide to Boats with ABOS
Whether you are a boat owner, in the market for a boat, or selling a boat, it is important to be knowledgeable about the different types of boats on the market. There are 8 major types which include: personal watercraft, stern drive, inboard, personal watercraft, pontoons, deck boats, houseboats, sailboats, and outboard. Simply by looking at a boat, it can be hard to distinguish the differences between certain types, such as inboard versus stern drive. This guide details the characteristics of each type and the respective subtypes in which they are classified.
Stern Drive Boats
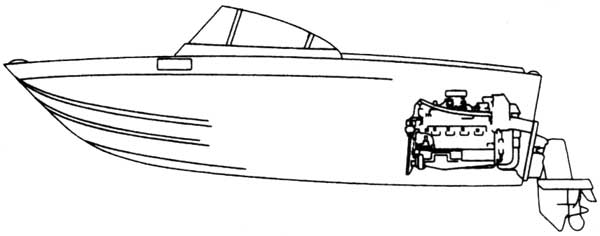
Stern Drive Boats, also referred to inboard/outboard, use a stern drive engine. Stern drive engines incorporate traits of both inboard and outboard engines. The construction of the engine is what distinguishes stern drive boats from other boats. While stern drive boats have a compartment that holds the engine, they also have an outdrive (transom unit) which makes them similar to outboard engines. They also have a propeller that serves as a rudder to steer and are usually in the form of runabouts or cruisers.
Inboard Boats
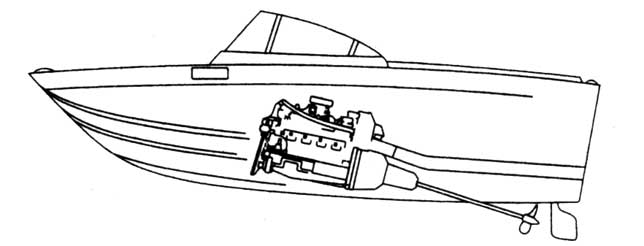
Inboard boats are just as they sound, boats with an inboard engine. The easy way to identify inboard boats is to remember that inboard engines are always in. Similar to automobile engines, these engines are powered by gasoline or diesel fuel. The transom is clear for inboard boats because the shaft, rudder, and props are beneath it. Inboard boats are most popular amongst fisherman and slalom skiers due to a lower center of gravity for fisherman and also produce a smaller wake which is preferred amongst the slalom skiers.
Outboard Boats
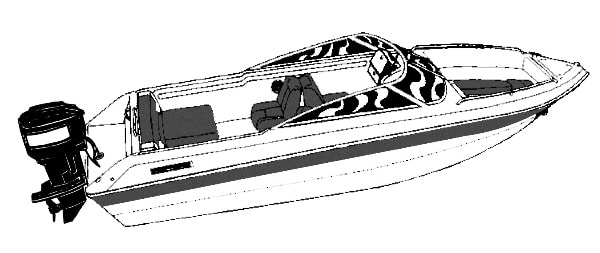
Outboard boats are powered by an outboard motor, which are portable engines enclosed in a gear case with a propeller attached at the bottom. Outboard boats’ motors are attached to the transom of the boat. A tiller (or steering wheel) swivels the entire motor.
Pontoons
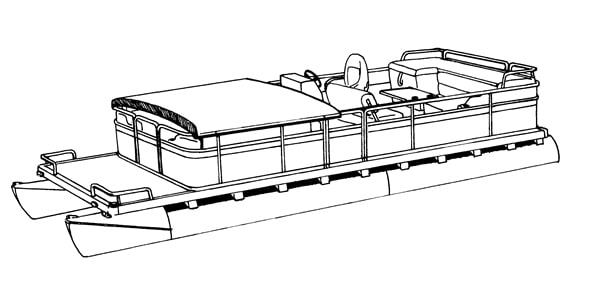
Pontoons are built for cruising at low to moderate speeds. A single flat deck and two tubes are the parts that make up a pontoon. Pontoons sit lower in the water which limits passenger capacity and performance capabilities. They are perfect party boats as well as excellent for swimming, grilling, and leisure fishing. Powered by outboard motors, pontoons are available in a large array of layouts due to the fact that they are modular. Pontoons are also available as Tritoons which are pontoons with three tubes.
Houseboats
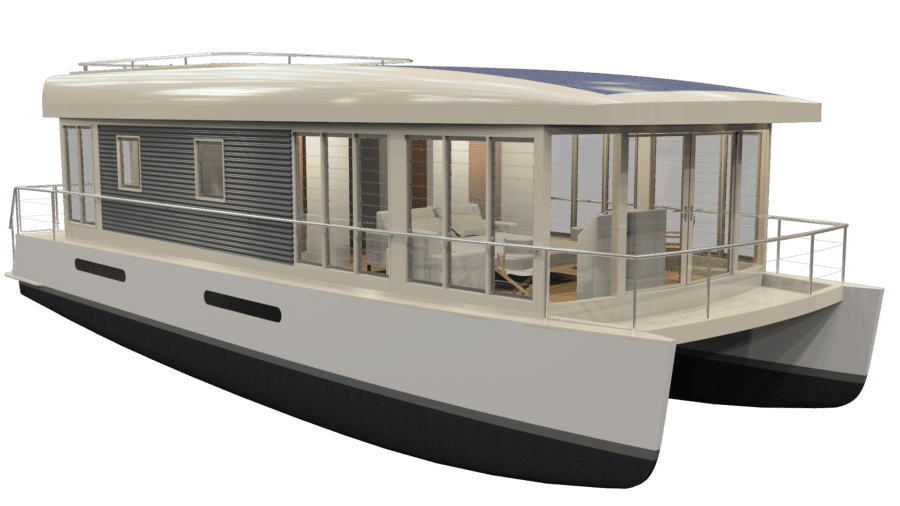

Houseboats, hence the name, are houses equipped for water. These boats have full kitchens, bathrooms, bedrooms, and living/dining spaces. There are two categories for houseboats, cruising (or bluewater) and non-cruising houseboats. Cruising houseboats are made with the option to go on excursions. These houseboats have sails or an engine which means they require a larger amount of fuel. Non-cruising houseboats have small engines or sails because they are not built for mobility. The non-cruising are the most popular style of houseboat and are anchored, moored/tied up to a slip in a dock or marina a majority of the time.
Sailboats
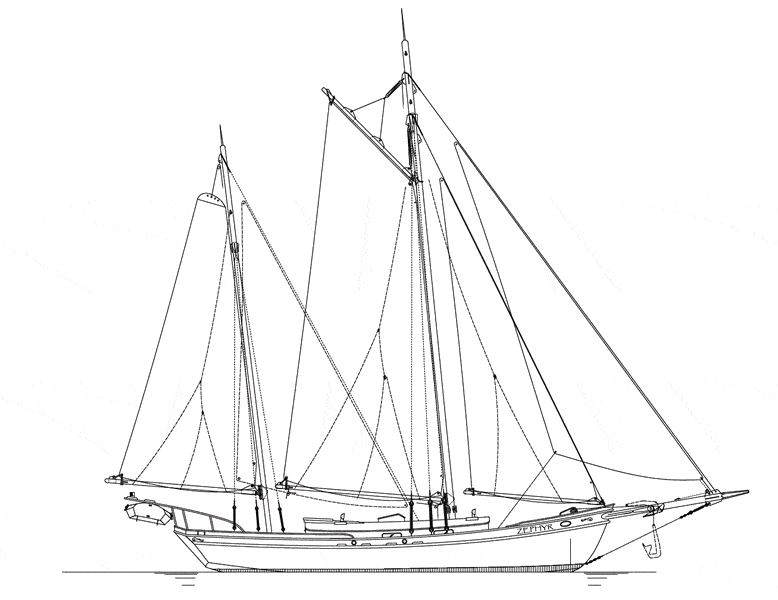
Sailboats, powered mainly by wind, have been around for centuries. Sailboats are boats that consist of sails, a mast, tiller, rudder, keel, boom, mainsail, jib, and hull. Sailboats float due to buoyancy, meaning the boat displaces an amount of water equal to its weight. There are 7 types of sailboats which include: cat, sloop, cutter, ketch, lateen, yawl, and schooner. The differences between these types of sailboats center around the placement and number of masts and sails on the boat.
Deck Boats
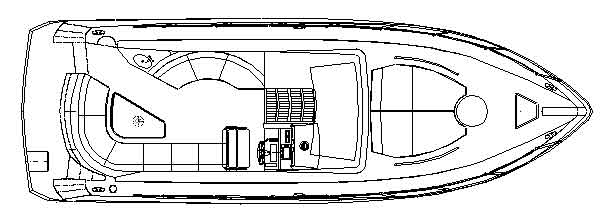
Deck boats are bowriders with extended (or stretched) seating. Unlike bowriders, with a v-shaped hull, the front of the hull on a deck boat is usually rounded or squared-off. Deck boats are mainly used for leisure cruising, water sports and fishing. Deck boats can be powered by outboard, inboard, or stern engines.
Personal Watercraft

Often referred to as a Jet-Ski, a brand of personal watercraft manufactured by Kawasaki, personal watercrafts are small inboard vessels equipped to hold 1-4 people. Modeled after snowmobiles, personal watercrafts consist of a saddle, handlebars, and powerful engines. These “boats” are used for touring/cruising, tow sports, and high performance.
Boat Subtypes
Within the main categories of boats covered in ABOS, some of these boat types are broken down into even more specific categories known as subtypes. This section details the subtypes of the 8 boat types covered above.
Stern Drive and Inboard Boats
Center Console: A boat with the helm on a console in the center
Cruiser: A boat with a cabin in the bow for overnight stay
Day Cruiser: A small cruiser with no cabin for overnight stay
Fish & Ski: Bowrider specialized for fishing and skiing
Racer: Small powerboat used for racing
Runabout: A small powerboat for multipurpose use (fishing, cruising, watersports)
Sports Cruiser: Cruiser with a single deck above the hull and cabin below. Also known as an express cruiser, these boats can go at high speeds
Sports Fisherman: Offshore fishing boats capable of high speeds
Ski: Boats designed for watersports that produce higher wakes
Sports Runabout: Runabouts capable of higher speeds than traditional runabouts
Trawler: Trawling is a type of fishing that uses a net. A Trawler is a boat specifically made for trawling.
Utility: Boats used for fishing or as work boats
Yacht: Medium- large recreational boats used for cruising or racing
Pontoon, Deck Boats, and Houseboats
Pontoon Boat: A boat with 2 aluminum tubes that support a deck
Pontoon Houseboat: A houseboat that is supported by tubes
Tritoon: A pontoon with 3 tubes
Full Hull Houseboat: Also referred to as V-hull houseboats, these houseboats are built for rougher waters
Sailboats
Cat: A sailboat with a single mast and a single sail
Sloop: A sailboat with 2 sails and 1 mast
Cutter: A sloop with a third sail in between the mainsail and headsail
Ketch: A sailboat with 2 masts, a shorter mizzen mast ahead of the rudder post
Lateen: A sailboat with a single triangular sail that runs in a fore and aft direction
Yawl: A sailboat with 2 masts, a shorter mizzen mast aft the rudder post
Schooner: A sailboat with 2 or more masts, the foremast and mainmast being the same height or the mainmast being taller
Outboard Boats
Bass Boat: Boats with a v shaped hull and low freeboard used for freshwater fishing
Canoe: A lightweight narrow boat with pointed ends
Center Console: A boat with the helm on a console in the center
Cruiser: A boat with a cabin in the bow for overnight stay
Dinghy: Small inflatable boats usually made of rubber
Day Cruiser: A small cruiser with no cabin for overnight stay
Fish & Ski: Bowrider specialized for fishing and skiing
Inflatable: Boats with sides that are inflatable tubes
Kayak: A type of canoe where passengers sit on the bottom of the boat
Racer: A small powerboat used for racing
Runabout: A small powerboat for multipurpose use (fishing, cruising, watersports)
Sports Cruiser: Cruiser with a single deck above the hull and cabin below. Also known as an express cruiser, these boats can go at high speeds
Sports Fisherman: Offshore fishing boats capable of high speeds
Ski: Boats designed for watersports that produce higher wakes
Sports Runabout: Runabouts capable of higher speeds than traditional runabouts
Utility: Boats used for fishing or as work boats
Boat Terms
There are many terms associated with boats and the way in which they operate. This section goes over the most important terms associated with boats that you will see when dealing with boats.
There are three types of boat engines – Stern drive, Outboard and Jet drive.
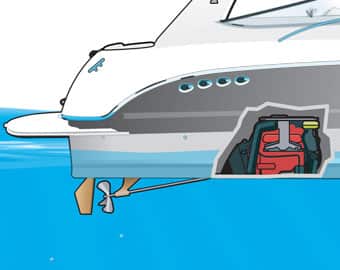
Stern (Inboard/Outboard): Stern drive boat motors are typically located within the main section of the under belly of the boat, while the propeller is located underneath the boat. Stern drive boats in turn have less exposure than an outboard motor.
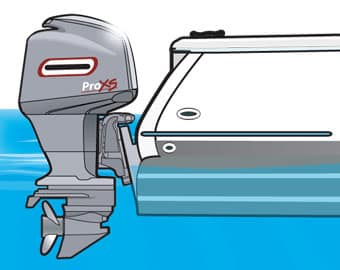
Outboard: An Outboard boat is one which the motor is on the exterior of the boat. Typically these motors can be physically seen on the back of the boat. Outboards are propelled with a metal propeller which can be lowered or raised in and out of the water (unlike Stern drive boat motors)
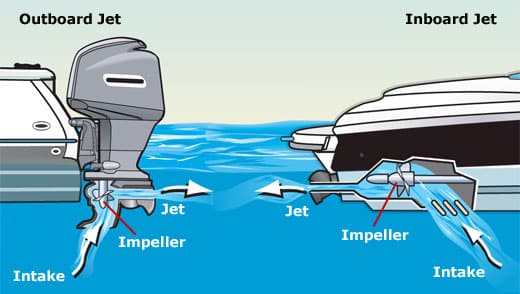
Jet propulsion: There are two different types of Jet propulsion engines – Outboard and Inboard. Outboard Jet propulsion engines are similar to Outboard motors yet they do not have a propeller. Rather have an impeller which intakes and outputs water in order to move the boat. Inboard Jet propulsion engines are typically located within the underbelly of the boat (like Stern drive boat motors). Inboard Jet propulsion engines propeller is located within the underbelly of the boat where the impeller intakes water and pushes it out through and external water exit.
Length: Extreme centerline length of hull
Beam: Extreme width of vessel
Weight: A unit or system of units used for expressing how much an object or quantity of matter weighs – the weight of the vehicle without cargo.
Hull: The frame or body of a ship or boat exclusive of masts, yards, sails, and rigging
Hull Material: The type of material used in the construction process of building the Hull of a Hull style boat. Usually Aluminum, Steel, or Fiberglass
Horsepower: A unit of power equal in the U.S. to 746 watts and nearly equivalent to the English gravitational unit of the same name that equals 550 foot-pounds of work per second
Pontoon Material: The type of material used in the construction process of building a pontoon boat. Typically Aluminum, Steel, or Fiberglass
Rig, Rigging: The system of ropes, cables and chains, which support a sailing ship or sail boat’s masts
Draft: Water depth required to float vessel (Centerboard or Dagger board down)
Displacement: Weight of water displaced by rigged vessel
Sail Area: Standard recommended working sail area. Does not pertain to the variously available oversize or undersize sails.
Bimini Top: Open-front canvas top for the cockpit of a boat
Trailer: A small vessel propelled by oars, paddle, sails, or motor for traveling, transporting good, etc.
Outboard motor: A small or medium-sized engine with a propeller that can be mounted outside the stern of a boat
Swim Platform: A wide platform at the transom equipped with a ladder to make reboarding easier.
Transom: The surface that forms the stern of a vessel.
Rudder: Mounted either on the transom or under the boat, the Rudder is a vertical blade that helps steer the boat.
Shaft: Transmits power from an engine to a propeller.
Props: Mechanical device for propelling a boat, consisting of a revolving shaft with two or more broad, angled blades attached.
Sources
https://en.mimi.hu/boating/swim_platform.html
https://www.hhprop.com/how-boat-props-work.php
https://www.boatcoversdirect.com/what-is-a-bimini-or-boat-top
http://www.boatingmag.com/boats/jet-drive-vs-sterndrive#page-10
https://www.boat-ed.com/pennsylvania/studyGuide/Outboard-and-Inboard-Engines;-Stern-and-Jet-Drives/101039_101039015/
http://www.michiganmotorz.com/marine-enginedrive-variations-a-10.html
http://forums.iboats.com/forum/general-boating-outdoors-activities/boat-topics-and-questions-not-engine-topics/642405-inboard-vs-outboard-boat
http://www.boatmania.com/semi-custom-cover-for-v-16-style-boats-length-16-6-width-86-motor-type-outboard.html
http://www.go2marine.com/product/152833F/pontoon-boat-semi-custom-covers-non-trailerable.html
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Houseboat_on_the_move_Monticello,_KY_10.JPG
http://www.boats.com/how-to/boat-buying-for-absolute-beginners-part-iv/
http://rvainsurance.com/coverage/marine/personal-watercraft/






